Creating HTTP Actions
This guide walks through creating an HTTP Action — from basic configuration to testing and output mapping.Prerequisites: You need a Flowripple account and at least one project.
Creating an HTTP Action
Configure the action
Fill in the basic info, request configuration, input variables, and authentication as described in the sections below.
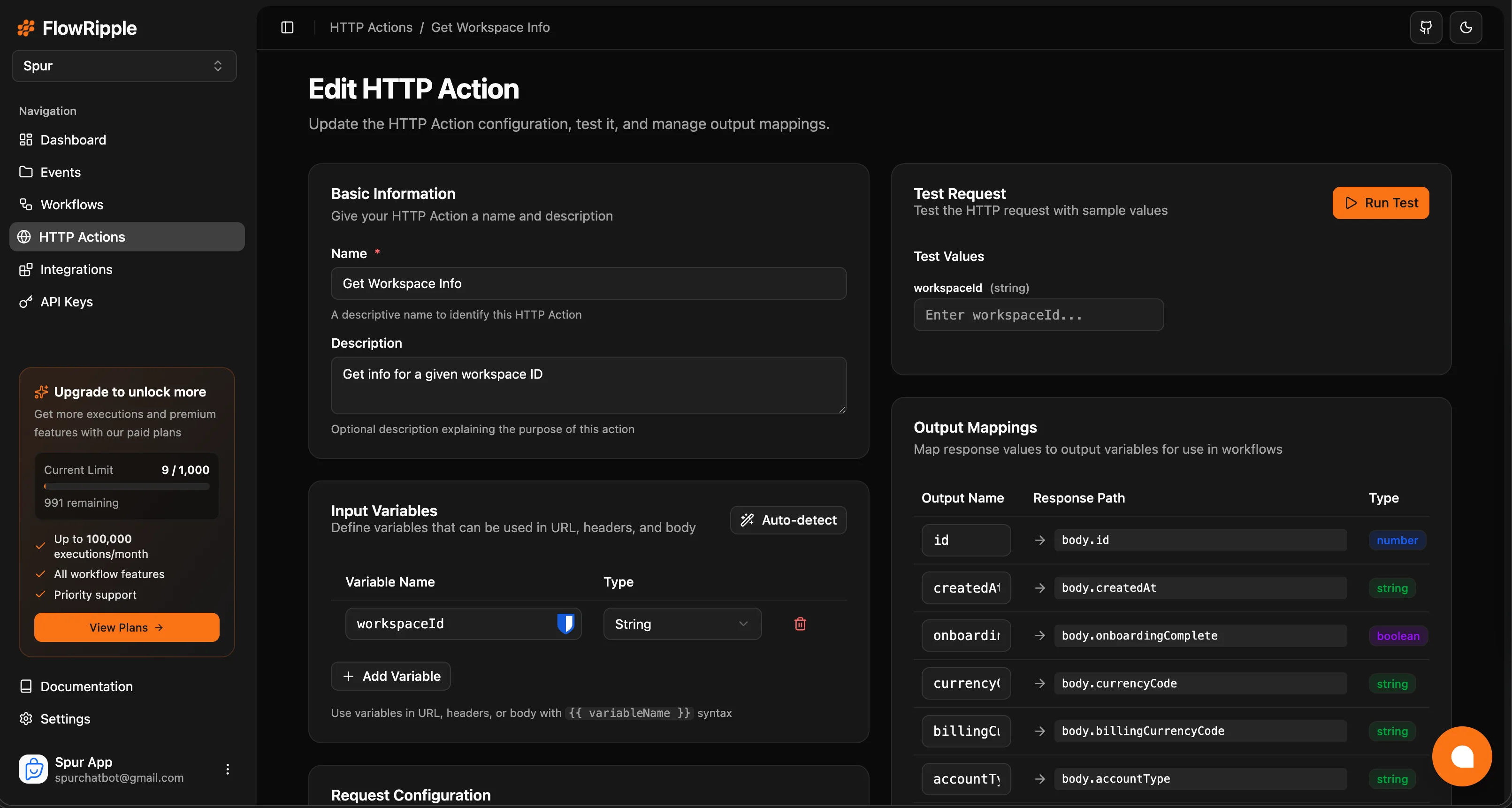
Basic Info
Configure the action’s name and description.| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Yes | A descriptive name (e.g., “Create Stripe Customer”, “Send Slack Notification”) |
| Description | No | Brief explanation of what the action does |
Request Configuration
HTTP Method
Select the HTTP method:- GET — Retrieve data
- POST — Create resources or send data
- PUT — Replace resources
- PATCH — Partially update resources
- DELETE — Remove resources
URL
Enter the full endpoint URL. You can use input variables in the URL:Headers
Add key-value header pairs. Both keys and values support input variables:Request Body
For POST, PUT, and PATCH methods, configure the request body. Body types:JSON
JSON
The most common format for REST APIs.
Form Data
Form Data
URL-encoded form data.
Raw Text
Raw Text
Plain text content.
XML
XML
XML-formatted data.
Input Variables
Input variables make your HTTP Action dynamic. They use the{{variableName}} syntax and can appear in the URL, headers, and body.
Auto-Detection
Click the “Auto-detect” button to scan your URL, headers, and body for{{variableName}} patterns. Detected variables are added to the input variables table automatically.
Manual Addition
Click “Add Variable” to manually define an input variable with a name and type.Variable Types
| Type | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| string | Text values | "usr_123" |
| number | Numeric values | 42, 99.99 |
| boolean | True/false | true |
| object | JSON objects | {"key": "value"} |
| array | JSON arrays | ["a", "b", "c"] |
Authentication
Configure how the action authenticates with the target API.None
No authentication headers are added.API Key
Sends an API key in a custom header.| Field | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Header Name | X-API-Key | The header name for the key |
| API Key Value | — | The key value (supports input variables) |
Bearer Token
Sends a Bearer token in theAuthorization header.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Token | The bearer token value (supports input variables) |
Authorization: Bearer <token>
Basic Auth
Sends Base64-encoded credentials in theAuthorization header.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Username | Auth username (supports input variables) |
| Password | Auth password (supports input variables) |
Testing
The test panel lets you run the action with sample values before saving.Fill in test values
Enter sample values for each input variable in the test panel on the right side of the form.
Run the test
Click “Run Test”. The action executes with your sample values and displays the response.
Output Mappings
Output mappings extract specific values from the API response and expose them as named variables in workflows.Creating Output Mappings
After running a test, click the ”+” button next to any value in the JSON response explorer. This creates a mapping with:| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Output Name | Variable name used in workflows | userId |
| Response Path | JSON path to the value | body.data.id |
| Type | Auto-detected data type | string, number, etc. |
Accessing Outputs in Workflows
Once mapped, output values are available in downstream workflow steps as:customerId, downstream steps can reference it as outputs.http.customerId.
Output mappings only work when the response structure matches the configured paths. Test thoroughly to ensure mappings extract the expected values.